Advancing Standardized Health Equity Quality Measurement
Measurement can help illuminate how well health plans are serving Medicaid enrollees, how equitable the care being provided is, and ultimately help drive improvement.
NCQA, with support from the California Health Care Foundation, undertook work to advance standardized health equity quality measurement. While this work focused on Medicaid programs, the findings have implications for other payers and settings as well. The grant, which lays the groundwork for an accountability infrastructure for equitable care measurement and reporting, had three objectives:
- Increase understanding of current health equity quality measure use and application among state Medicaid programs.(December 2021 White Paper: Evaluating Medicaid’s Use of Quality Measurement to Achieve Equity Goals)
- Recommend a common set of health equity quality measures, by domain, that state Medicaid programs (and potentially other purchasers) can leverage as part of accountability and value-based payment programs. (September 2022 Report: Advancing Health Equity: A Recommended Health Equity Framework for Accountability in Medicaid)
- Evaluate health equity measure composites and summary scoring concepts for use in Medicaid program accountability. (February 2023 Issue Brief: Measuring Health Equity: A Review of Scoring Approaches)
Advancing Health Equity: A Recommended Health Equity Framework for Accountability in Medicaid
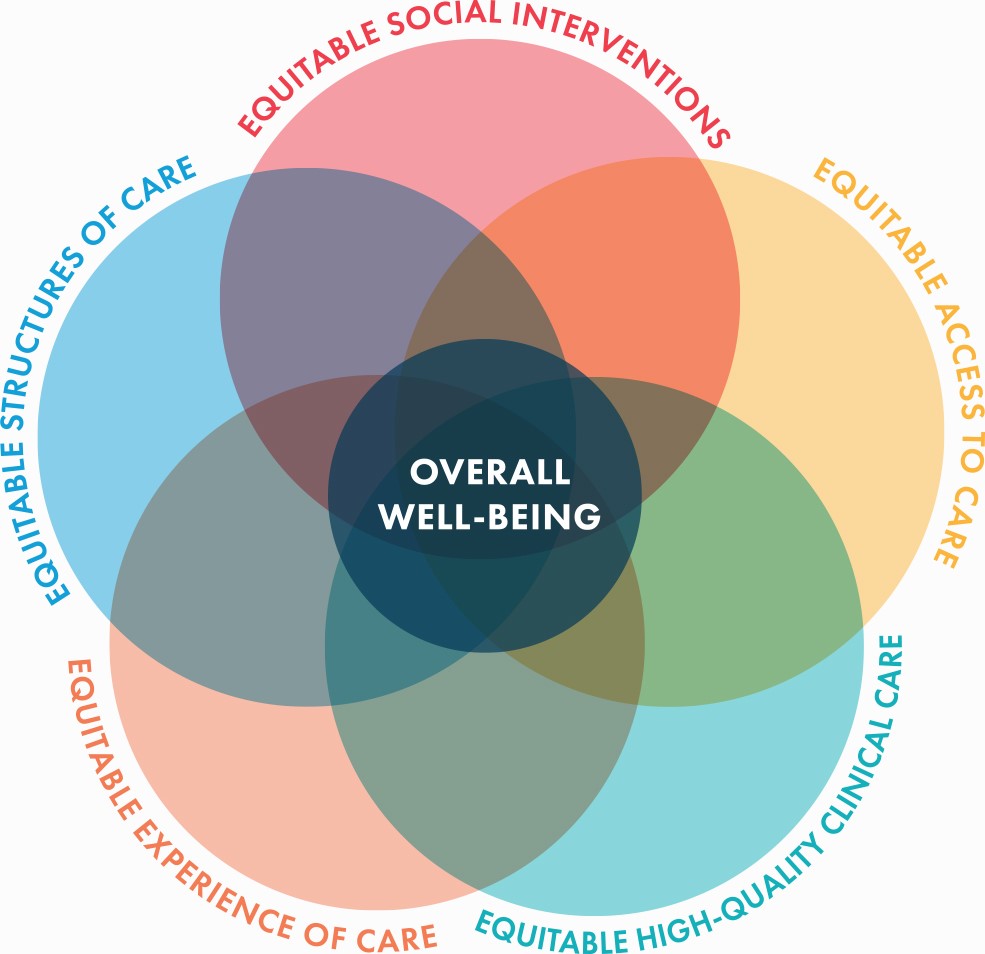
Advancing health equity is a national priority, and Medicaid programs are at the forefront of this effort. Communities that experience health inequities are often faced with social conditions that create barriers to achieving their best health; Medicaid enrollees are more likely to be a member of these communities. This can include food insecurity, housing instability, limited community resources, and structural and interpersonal racism. All of these conditions and their effects have been highlighted and intensified by the COVID-19 pandemic. Quality measurement is a key accountability tool in most Medicaid programs. NCQA developed a health equity measurement framework that can be used by state Medicaid programs for accountability in health plan managed care contracting. The framework provides a list of six core quality domains, each with two to five associated quality measures.
To develop the framework, the authors examined peer-reviewed and grey literature, conceptual and measurement models, policy statements, and state contracting documents, to identify themes, priorities, gaps, and opportunities. The framework was further developed by engaging with stakeholders including representatives from state Medicaid agencies, Medicaid managed care organizations, community-based organizations, patients and patient advocates, researchers, and others. The framework prioritizes racial equity but is designed to expand beyond race and ethnicity. While this framework focuses on Medicaid, many of its elements can be applied across the health care ecosystem.
"*" indicates required fields
Interested in hearing more?
- Read our recent blog on highlighting the framework.
- Listen to representatives from a state Medicaid agency discuss the framework and its breadth.
- Watch a webinar recording and view the slides from our webinar, Advancing Health Equity: A National Conversation on a Measurement Framework for Accountability in Medicaid. The webinar provides an overview of the framework as well as reactions from state, plan and consumer perspectives.
Issue Brief: Measuring Health Equity: A Review of Scoring Approaches
To understand how we can quantify health equity, NCQA reviewed four approaches to health equity measurement that states’ Medicaid programs could consider as they adopt scoring approaches that measure equitable care and outcomes. This issue brief covers four key selection criteria to determine which approach to use to measure equitable care:
- Select indicators of social determinants of health.
- Select a reference group (a “standard” comparison group independent of the data vs. the data informing the comparison group).
- Select health care quality metrics. These could include composites (e.g., vaccination rates, quality measures, infant mortality rates).
- Use benchmarks (e.g., compare results to national estimates).
The four approaches are similar in how they underscore key dimensions for measuring equitable health care quality and outcomes, and can lay a foundation for a diversified measurement landscape. They are an important starting point when considering scoring approaches to health equity.
Download the issue brief today by filling out the form below.
"*" indicates required fields
White Paper: Evaluating Medicaid’s Use of Quality Measurement to Achieve Equity Goals
An increasing number of states use explicit equity measurement and accountability in their managed care programs. This white paper, released in December 2021, examines state Medicaid program’s current health equity efforts, also suggests a common language around intent, goals, methods, and expectations, and may help move the needle towards accountability for equitable care.
The authors examined peer-reviewed and grey literature, review state contracts and public policy statements and conduct interviews with seven state Medicaid representatives. Their paper focused on five themes:
- State Medicaid approaches to overall equity strategy
- Priority populations and areas of focus
- Use of measurement
- Health plan accountability and evaluating performance
- Stakeholder and community engagement
Download the white paper today by filling out the form below.
Interested in hearing more? Members of the project team discuss findings and implications in the NCQA blog.
"*" indicates required fields
This work was supported by the California Health Care Foundation (CHCF), which works to ensure that people have access to the care they need, when they need it, at a price they can afford. Visit www.chcf.org to learn more.

