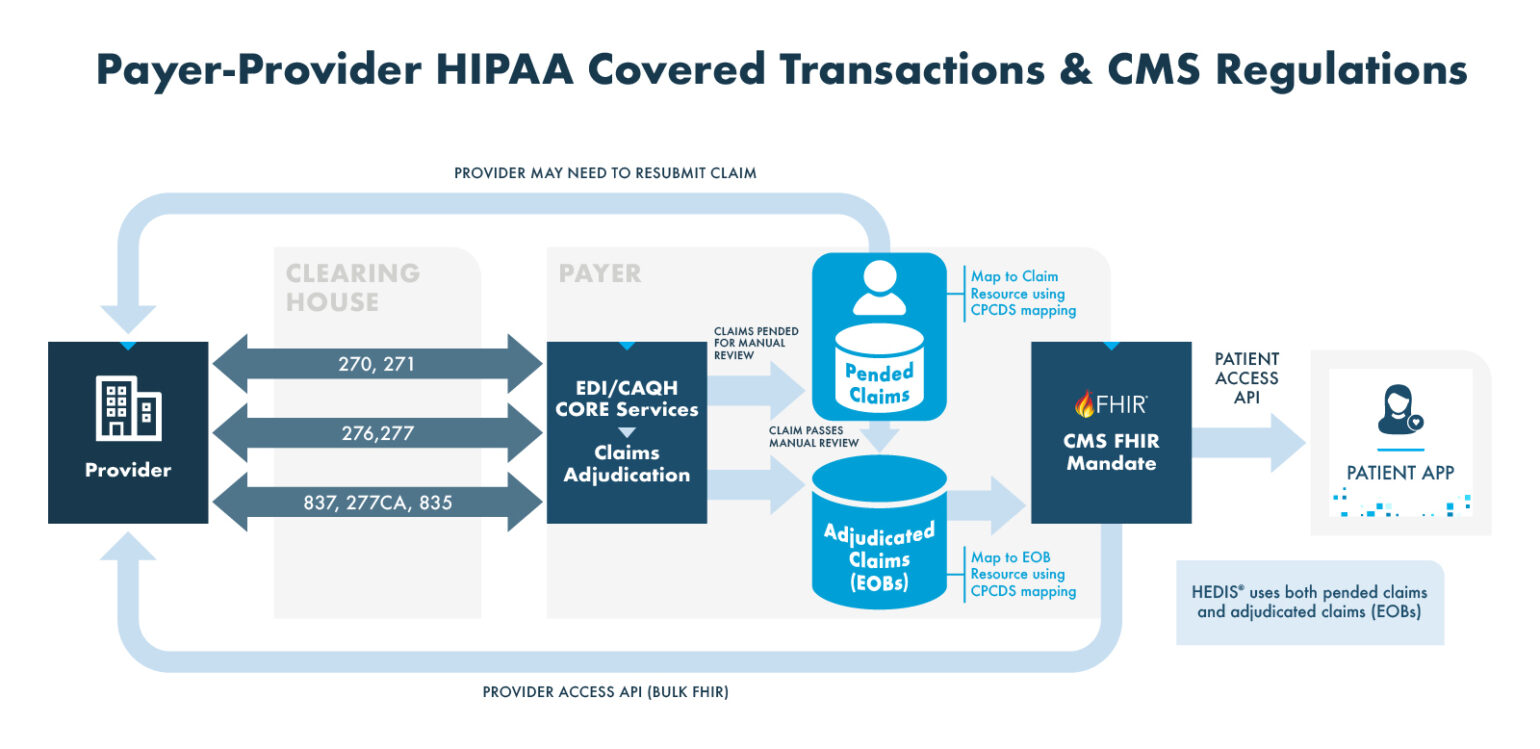
FHIR Supports Interoperability and Data Standardization
Organizations must ensure their data are clean, structured and accessible, in order to generate accurate insights and enhance their decision-making process. Preparing the data also mitigates errors, inefficiencies and compliance issues, and ultimately enables a more agile and responsive environment.
Fast Health Care Interoperability Resources (FHIR®) is a standard developed by Health Level Seven International (HL7®) for exchanging health care information electronically. FHIR is designed for sharing health care data across systems and platforms, facilitating interoperability. This makes it an essential tool for developers and health care providers. FHIR-enabled interoperability supports improved patient outcomes by ensuring that all providers have access to the same current information, thus reducing errors, avoiding redundant tests and enabling coordinated care.
The importance of FHIR in digital quality assessment and health care interoperability cannot be overstated. By standardizing the format and exchange protocols of health care data, FHIR ensures that critical health information is consistently available, accurate and actionable. This enhances the ability of health care providers to conduct comprehensive digital quality assessments because they can access and analyze data from diverse sources seamlessly.
Understanding FHIR Data Requirements
FHIR uses a modern web-based suite of Application Programming Interface (API) technology, which allows developers to build applications that can access data from EHRs and other health care systems. FHIR supports RESTful (representational state transfer) architectures, making it flexible, scalable and easier to implement than previous standards. This interoperable approach to health care data exchange addresses many limitations of traditional data formats, and paves the way for more efficient and effective health care information systems.
Traditional Data Formats vs. FHIR
| TRADITIONAL FORMATS | FHIR | |
|---|---|---|
| FLEXIBILITY AND MODULARITY | Older health care data formats, such as HL7 v2 and CDA, tend to be rigid and complex, and often require significant customization to fit specific use cases. | Modular design allows greater flexibility. Resources can be easily extended and adapted to meet specific needs without altering the core standard. |
| EASE OF IMPLEMENTATION | Can be challenging to implement due to their complexity and the need for specialized knowledge. | Use of standard, modern web technologies, like RESTful APIs and JSON/XML, simplifies implementation. |
| INTEROPERABILITY | Often require significant effort to map and translate data between different systems. | Standardized resource definitions and use of common web protocols reduce the need for complex data transformation. |
| DATA EXCHANGE | Data exchange often relies on batch processing and point-to-point integrations, which can be slow and prone to errors. | Supports real-time data exchange through APIs, enabling faster and more reliable communication between systems. |